In this article we shall try to comprehend the marvel of nature that is reason for our existence, Our Sun.
Sun is the reason for existence of all the forms of life on earth and it is the ultimate source of energy. Be it in form of fossil fuels, oil and natural gas, all forms of energy that human civilization uses today can be traced back to sun. Still most of us seem to have no idea of how the sun generates so much energy.
I shall explain the overall process (parts of which are still under study) of how sun creates such huge amounts of energy to sustain itself. How does sun create the heat that can be felt even from a distance of 149.6 million kilometers and how it emits light which we can see with our eyes.
Core of Sun – The Energy Factory
In the heart of sun resides a nuclear factory with temperature as high as 15.7 million kelvins. This is the place where the energy required to sustain a fireball weighing 1.989 *1030 kilograms is generated.
Nuclear fusion takes place in the core of sun by following a proton-proton chain. In the p-p chain two Hydrogen atoms are fused to create a Helium atom and energy is liberated in this process. Energy that is produced is in form of small packets. These packets are called photons and have a fixed amount of energy in them given by, E= h*f. (h = Planck’s constant, f = frequency)
The following image shows a proton-proton chain releasing energy in form of Gamma rays.
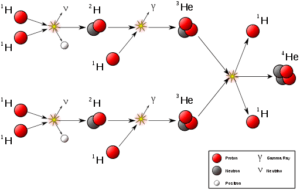
Image Attribution: Doctor C / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)
Journey begins
Our packet of energy which we will now call photon has born out of the nuclear furnace in core of Sun and is now ready to travel far in space.
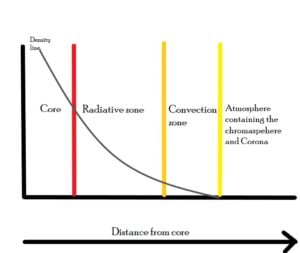
The Gamma rays released in form of photons are now entering the ‘radiation zone’ of sun. The radiation zone is a very dense zone packed with matter. In-fact it is so dense that photons can barely travel a short distance (maybe a 100 or so atoms) before they are absorbed by another atom.
The Struggle
The energy produced in core starts travelling outwards in form of a constant stream of photons which seem to be jumping between atoms. As photons jump among atoms they lose energy in form of heat which makes sun grow hot. It takes a photon nearly 170,000 years before it crosses the radiative zone and reaches the outer layers.
As our photon which once had energy enough to be classified as Gamma ray starts jumping between atoms it loses energy in the process of continuous absorption and reabsorption. This loss of energy not only heats up sun but makes the frequency of the photon drop. As we know energy is given as, E = h*f here ‘h’ is a constant hence if energy is being lost frequency is getting smaller.
This phenomenon of loss in frequency changes the status of photon when it reaches the outer layers of sun. The photon once we had seen taking birth as a gamma ray has now lost some energy and has become a part of vast electromagnetic spectrum.
The electromagnetic spectrum emitted by sun in increasing order of frequency is explained below.
- Radio waves – Sun emits radio waves at a certain frequency that can be used by astronomers to study Sun’s atmosphere.
- Microwaves- These are the same rays that give you warm and cooked food every day.
- Infrared waves – The reason why it feels warm while standing in sun.
- Visible light – The part of EM spectrum that you can see. Although it is very small this is only part which we can observe with our eyes.
- Ultraviolet rays – Slightly high energy rays capable of causing skin cancer. They get blocked by our now depleting ozone layer.
- X rays – Although very less but the gases in corona of sun do emit X rays.
Sun – The Cosmic Teapot
Our photon has crawled through the 70% of sun’s radius for a very long time and is finally free!
It has reached the outer layer of sun and luckily here the density is low enough for convection to take place. So how does convection work inside sun?
It works the same way it helps you boil water in the tea pot at your home…
Principle of convection states that.
When a liquid is heated it expands and rises above, leading behind a partial vacuum near bottom which gets replaced by the cool liquid coming from the top.
In Sun hot plasma rising from the inside of Sun expands as it gets hotter and rises to the surface and the cool surface plasma soon drops behind to fill the partial vacuum and it gets re-heated again.
Hence, you can say in principle 30% of sun is just a giant cosmic teapot.
As the packets of energy rise with the plasma through the rest of remaining sun they experience a rapid fall in density and temperature. In-fact the density at surface (near photosphere) of sun is just 0.2 g/ m3 which is 50,00,000 times less dense than water itself!
Freedom!
The packet of energy has now traveled 695,842 km, half way through radiation like a photon and halfway through convection in form of heat energy. It is now finally ready to be launched in space as a photon.
We have entered what scientists call photosphere. This is the region of sun which is seen by our eyes when we look at sun. The photosphere is the portion where photons are created and where they leave the Sun forever.(their home for nearly 1,70,000 years)
As photons have started moving ahead the regions start changing rapidly. As photons race through Sun’s atmosphere at speed of light they experience drastic changes. The atmosphere cools down at once as we rise above the surface but a drastic transition occurs and the temperature suddenly starts soaring high back again.
The accurate reason for what I am describing in this part are not yet known
Our photons rise above sun and the temperature cools down from 5000K to 4100K. But as soon as it enters an atmospheric zone called chromosphere the temperature starts rising again. This is mainly due to the ionized gases in atmosphere present due to huge swarm of photons bombarding them.
The effect of continuous bombarding is such that temperature of Corona (the outer atmosphere) is nearly 2 million kelvins and sometimes during large amounts of solar activity the temperature of Corona can rise up to 20 million kelvins!
Corona is clearly visible during a total solar eclipse, though it is not advisable to look at it directly.
Destination appears…
Now that it has crossed the violent atmosphere of sun, the journey of the photon becomes smooth and after 8 brief minutes of calm the photons emitted from sun face an obstacle in form of the Earth’s atmosphere.
As photons start penetrating the atmosphere the high energy photons start interacting with gasses in our atmosphere and they form the ionosphere. Ionosphere is a layer created by ionization of gaseous molecules on reaction with photons from sun. We use this layer to reflect the radio waves and send signals on earth.
Since we have selected a visible range photon this photon passes through the above ionosphere quite unhindered. As the photons start penetrating deeper and atmosphere starts becoming denser, we see that there is a sudden fall in UV rays.
This effect of sudden vanishing of photons in UV range my friends is work of ozone layer in stratosphere. The ozone absorbs the UV rays and prevents us from their deadly effect on humans. The photons are now about to approach the surface when blue light photons start hitting particles.
As particles get bigger in size near ground the blue light with a small wavelength finds it harder to get around them and gets scattered of by hitting them. This scattering is known as Rayleigh scattering and is the reason why sky appears blue when we look up in day.
The Final Realization.
The great 1,70,000 years long journey of a photon has finally come to an end.
The photon has suddenly hit the retina of a human’s eye who was coincidentally looking up at the sky at the same time.
The nerve cells on retina have transformed the energy contained in a photon into an electrical signal. This signal is interpreted by brain which will finally decide what color it represents.
And with this I conclude my story of a photon from birth to end. I hope you appreciate nature’s grand design every time you look up in the sky. 😊
Evanesco…
Featured Image Source: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Csm_WieSo_Verlust_Masse_Sonne_f6d924ecef.jpg
Featured Image attribution: Test / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)




